Rektocele
Colorectal Diseases
/
Prof. Dr. Gokhan CIPE
What is Rectocele?
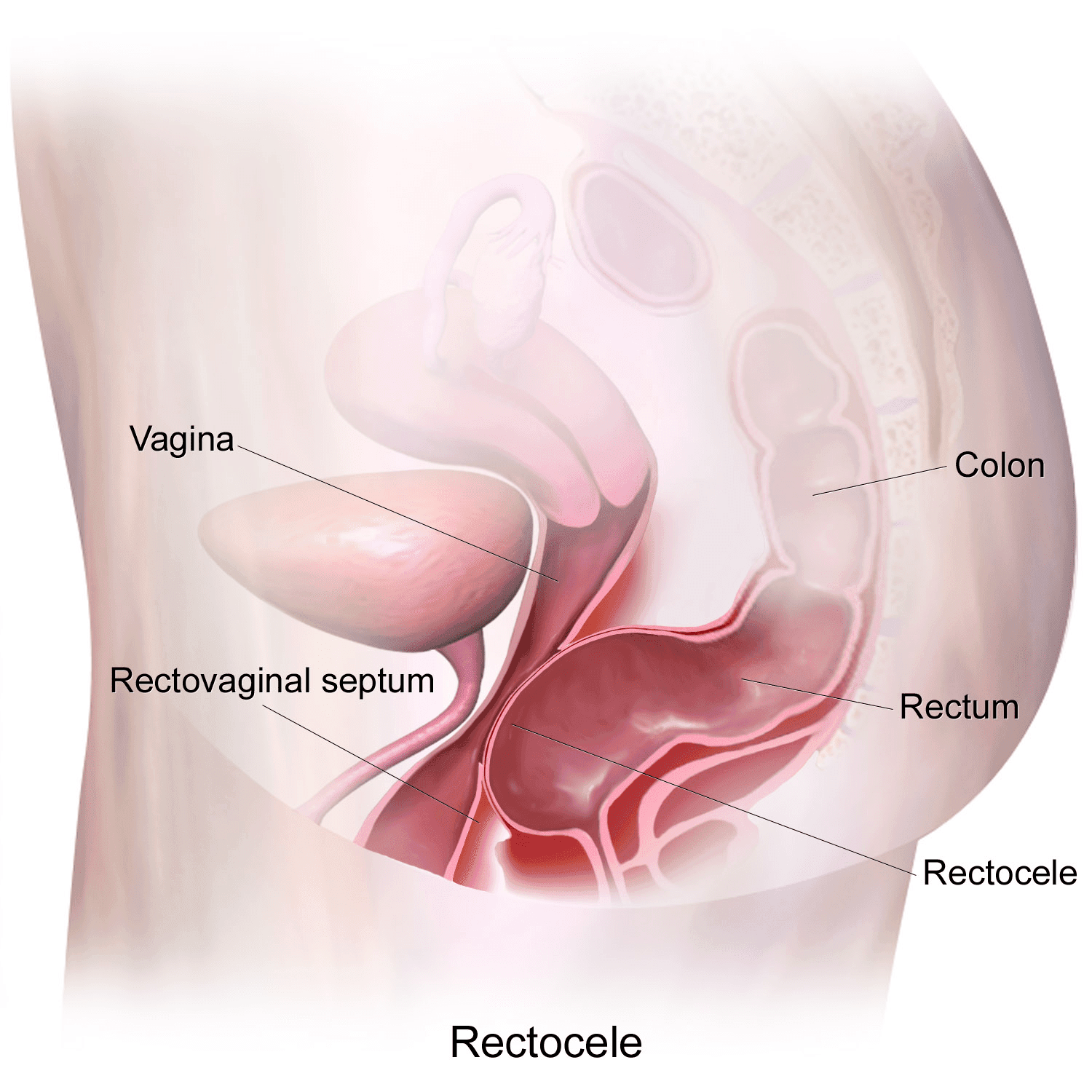
It is the extension of the anterior wall of the rectum towards the vagina. Most rectocele is seen in women. It can be seen in men, though rare. In some patients, the rectocele may be seen as part of the general weakness of the pelvic floor muscles. Uterine or vaginal prolapse, rectal prolapse, feces or urinary incontinence may accompany.
What are the causes of rectocele?
The underlying cause is weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and thinning of the rectovaginal septum. There are several risk factors for rectocele in women. These; This is because there are numerous vaginal births, difficult births, episiotomies, constipation history. Uterine removal is also a risk factor for rectocele. Although it is frequently seen in the elderly, it can also be seen in young people and those who have never given birth.
What are the symptoms of rectocele?
Symptoms may be vaginal or rectal. Vaginal symptoms; external compression of the vagina, palpable mass in the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse, vaginal bleeding can be seen in advanced stages.
Rectal symptoms;
- Constipation,
- Forced defecation
- Unable to discharge fully.
Sometimes during defecation, swelling that grows into the vagina is seen. Some women notice that when they step on the back wall of the vagina, they are more easily defecated.
How is Rectocele Recognized?
Most rectoceles are recognized by examination of the vagina and rectum. However, it is difficult to evaluate the degree and size of rectocele by examination. The appropriate method for diagnosis is defecography. With this method, rectocele size and straining and how much rectum is emptied can be seen.
What are the treatment options for rectocele?
There is no need to treat rectocele, which does not cause any complaints. In general, patients with rectocele should consume high-fiber foods and avoid constipation by drinking plenty of water.
Medical treatment
Feed on high-fiber foods and drink plenty of water. The fibers absorb water like a sponge, causing softer defecation.
Avoid sitting in the toilet for a long time. If it is not completely emptied, take a break and try again later. Pressure against the rectocele can sometimes be beneficial by pushing the feces into the correct path.
Surgical treatment
If symptoms persist despite medical treatment, surgical treatment may be necessary. There are various surgical techniques for the surgical treatment of rectocele. Rectocele treatment can be performed from the anus, vagina, anus and vagina, or from the abdomen.
Colorectal Diseases
Robotic Surgery
General Surgery
