Obesity Surgery
General Surgery
/
Prof. Dr. Gokhan CIPE
What is Obesity Surgery?
Obese disease is a disease in which fat tissue increases to the extent that it is harmful to human health. If one’s body weight is 20% higher than normal, that person is considered obese. If the Body Mass Index (BMI) is between 25 and 29.9, it is considered overweight, and 30 or more is considered obese.
Why do people become obese?
- Getting more calories
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Not getting enough sleep
- Consumption of foods that inhibit lipid metabolism
- Endocrine disorders
Obesity Related Diseases
- Bone and cartilage degeneration (Osteoarthritis)
- Coronary heart diseases
- Gallbladder diseases
- High total cholesterol, elevated triglyceride degree (dyslipidemia)
- Respiratory problems
- Sleep apnea
- Hypertension
- Type 2 diabetes
- Various types of cancer
In the laparoscopic procedure, surgeons make small incisions (5 mm – 10 mm) to reach the abdominal cavity via trocar (small surgical instruments like tubing). The laparoscope, which is connected to a small video camera, is inserted into a small trocar. The resulting image is projected onto a TV screen, giving the surgeon an enlarged view of the stomach and other internal organs. 5 to 6 small incisions are made and trocars are placed to use special surgical instruments to perform the surgery. All surgery is performed in the abdomen after the intra-abdominal cavity is inflated with carbon dioxide gas. When the operation is over, the gas is taken out.
Nutritional Changes; It is recommended for obese patients to reduce the daily calorie rate and to use more fruits, vegetables and whole grains. It is important that the diet be varied. You should not limit yourself to taking advantage of various dishes and flavors. In nutrition, sugar, purified carbohydrates and adipose tissues need to be significantly reduced.
Physical Activity; The more the body moves, the more calories burn. To remove 1 kg of fat, 8,000 calories must be burned. For obese patients, fast walking is the best way to increase physical activity. The combination of a good diet with high physical activity increases the chance of a gradual and controlled weight loss.
Drug Treatment to Lose Weight; If the patient has difficulty in losing weight or if obesity has a serious impact on his health, he may seek medical treatment. Drug treatment should be used in obese patients if:
When all other ways to lose weight fail, if the patient’s BMI is above 27 and he has diabetes, hypertension or sleep apnea, the patient’s BMI is above 30.
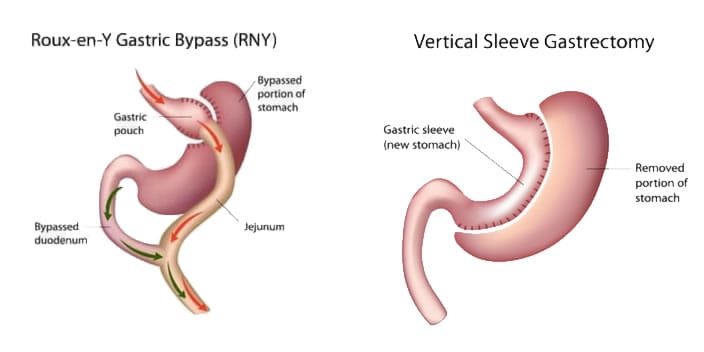
It is aimed to reduce the stomach volume (about 60-100cc) and thus make the patient feel satiety with very little food. For this purpose, a certain portion of the stomach is surgically removed and a tubular (about the size of a banana) stomach is left behind. In addition, the appetite-controlling ghrelin hormone is under-produced and therefore the patient’s appetite for food is reduced. However, sleeve gastrectomy surgery does not affect the digestion of calories and nutrients in the intestines.
It is performed by laparoscopic method like other obesity surgeries. Surgery is performed by entering small incisions in the abdomen. The stomach is reduced and anastomosed to the small intestine. Thus, the stomach is reduced, as well as the absorption of nutrients is reduced.
Like the sleeve gasrectomy, this process starts with removing most of the stomach. The surgeon then closes the middle part of the intestine and connects the last part to the duodenum. This is called the duodenum switch.
The divided part of the intestine is not removed from the body. Bile and pancreatitis are connected to the end of the intestine so that gastric juices flow into this part of the intestine. This is called biliopancreatic diversion. After such changes, many meals do not enter the small intestine and thus less calories and nutrients are digested. This leads to weight loss with a smaller size of the stomach
The success rate in weight loss is reported to be slightly higher in gastric bypass surgery than tube gastric administration; however, all techniques have shown good or excellent results. Many reports report a 40-50% weight loss for sleeve gastrectomy and 65-70% weight loss for gastric bypass after 1 year.
Weight reduction generally persists in all surgeries for 18-24 months after surgery. It was common to gain some weight after about 2 to 5 years after surgery
Obesity surgery is recommended for patients with a body mass index of 40 or more and who cannot be undermined by methods such as medical nutrition, exercise and medical treatment under expert supervision.
In addition, it is recommended for patients with a body mass index of 35 or more, which affect the patient’s quality of life and duration, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, sleep apnea. Which surgery is appropriate is determined by various examinations and tests
In the reported case series, the sudden death rate after laparoscopic obesity procedures is very low (below 1%). On the other hand, complications such as wound infections, wound opening, abscesses, stapler opening and leakage, intestinal rupture, intestinal obstruction, large ulcers, pulmonary problems and formation of blood clots in the legs (5-10%) are also less common in tube gastric surgery.
Other problems that may require additional surgical procedures may occur in the postoperative period. These problems include enlargement of the sac, persistent vomiting, stomach pain or inability to lose weight.
After gastric bypass, deficiencies of nutrients such as vitamin B12-folate and iron may be seen. Taking the necessary vitamins and nutritional supplements often prevents them.
Another potential consequence of gastric bypass is dumping syndrome. Dumping syndrome; It is characterized by abdominal pain, cramping, sweating and diarrhea after consumption of foods with high sugar content.
Avoiding foods with a high sugar content prevents these symptoms. After malabsorption surgery, nutrient deficiencies and protein deficiency are observed similar to those seen after gastric bypass. Diarrhea or loose “feces sık are frequently observed after malabsorption surgery, depending on the amount of fat intake.
Body Mass Index Calculator
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of your weight proportional to your height. Use this easy tool to calculate your BMI.
Colorectal Diseases
Robotic Surgery
General Surgery
